Web Vitals – new Google ranking factors
The Google update focuses on user experience. How to push your website with Web Vitals

Anyone who is concerned with ranking factors will not be able to avoid web vitals in 2021: the term currently characterises all relevant forums, blogs and websites.
But what are web vitals actually? In November 2020, Google announced an update that will significantly change the rankings: the Web Vitals. After the announcement in November 2020, these will be rolled out from May 2021 and will have a significant influence on the rankings.
Web Vitals simply explained
Roughly speaking, this update means that the user experience of a website will become more important in Google's ranking. This is Google's reaction to its own studies, which show that the UX has become significantly more important for 70 percent of users in 2020.
A Google update can normally include a lot – however, the company announced the Web Vitals long in advance and even named quite precisely how website operators should react.
The Web Vitals in detail
The graphic below shows which factors count for Google after the update.
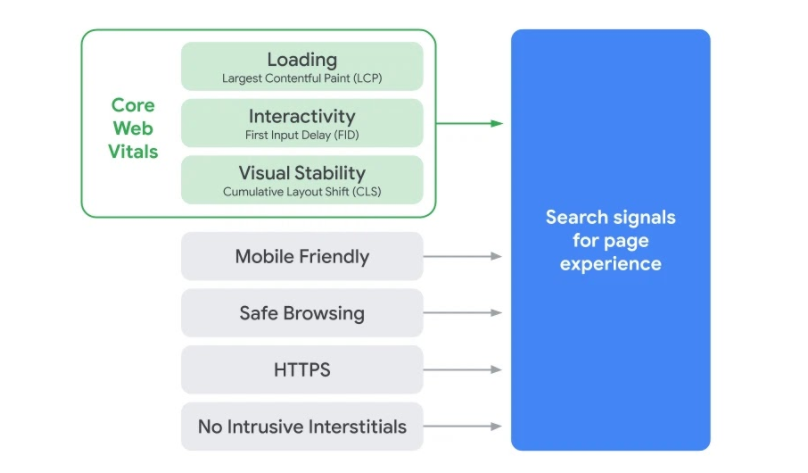
As the graphic above shows, there are three central Core Web Vitals:
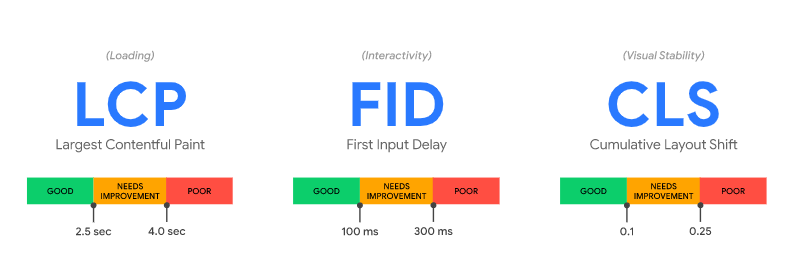
- Loading = Largest Contentful Paint (LCP). This is about how quickly the main content becomes visible to the user. First Contentful Paint (FCP) is out – at least for Google. It is now more important that the main content is displayed and not just the first fragment as with FCP. Google measures the duration in seconds. The scale is very simple: anything under 2.5 seconds is good. A response time between 2.5 seconds and 4 seconds is considered average and more than 4 seconds is bad.
- Interactivity = First Input Delay (FID). How quickly the user can interact with the page becomes more important in Web Vitals. Here Google measures the duration between the user interaction and the browser reaction. Here, 0.1 seconds is considered good, up to 0.3 seconds is considered medium and anything over 0.3 seconds is considered poor.
- Visual Stability = Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). This factor assesses the visual stability of the page and whether the page content jumps – for example, due to asynchronous loading. Here, too, good means up to 0.1 seconds, up to 0.25 seconds medium and anything over 0.25 seconds bad.
Your website should also be mobile friendly. However, this already applies since April 2018 and mobile-first indexing. Use HTTPS as the website standard. Also avoid interstitials – i.e. advertising banners that are displayed to the user before he opens the website.
So much for the numbers and terms. In the next paragraph, I will explain what you can do to make your website fit for the Web Vitals.
Need for action: This is what the Core Web Vitals mean for SEOs
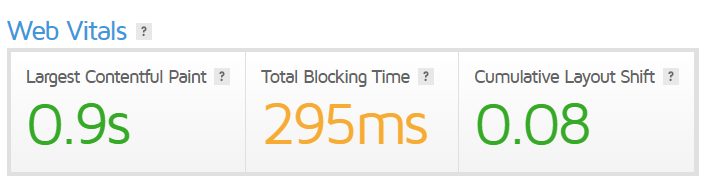
1. Measure values
In the first step, you should measure the values mentioned above. The most accurate tools are from Google - for example:
- PageSpeed Insights
- User Experience Report
- Lighthouse
- Google Search Console (Core Web Vitals Report)
In the meantime, other providers have also taken up the topic of web vitals and added corresponding features. For example, you can query your values with the following tools:
Based on your values, you can then optimise the Core Web Vitals in particular.
2. Eliminate sources of error
Common sources of errors and optimisation points are:
- Server response times are too slow (LCP).
- Java Script and CC block rendering (LCP).
- Resources load too slowly (LCP).
- Javascript execution time too long (FID).
- Interactions are not prioritised; important code elements do not load at the beginning (FID).
- Provide images and ads in correct sizes (CLS).
- Different fonts (CLS).
Don`t forget UX
In contrast to the quite hard factors such as LCP, FID and CLS, the other aspects of web vitals are not only of a purely technical nature. User-friendliness for mobile devices is mainly influenced by the UX. User signals such as time on site, the bounce rate or the number of sessions are essential factors for a good UX for Google.
You need a UX concept to be convincing in the Google ranking: only through an excellent user experience can you achieve top values in the user signals. UX and SEO must therefore work closely together – because this is the only way to achieve an optimal result for users and the search engine.
My conclusion: Everything new?
As loudly as Google announced this update and as big as the echo in the SEO scene was, one might think so. However, all the factors of the Web Vitals are not new.
They were already important before the Google update.
The Web Vitals are now considered essential ranking factors. Ideally, you have already optimised these factors before - if not, you should urgently address these issues now. There is still enough time to address all the points raised in order not to lose good rankings.
Check your web vitals with the tools mentioned and then take appropriate measures. Happy optimising!
Would you like to learn more about SEO or are you interested in an SEO or UX concept? Do you need support to become fit for the Web Vitals? We are happy to help! Contact us today.